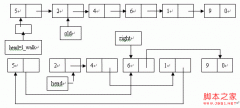
数据结构C语言实现系列――队列[组图]
Word-BREAK: break-all; PADDING-TOP: 4px; BORDER-BOTTOM: windowtext 0.5pt solid"> #includestdio.h #includestdlib.h typedefintelemType; /************************************************************************/ /*以下是关于队列链接存储
Word-BREAK: break-all; PADDING-TOP: 4px; BORDER-BOTTOM: windowtext 0.5pt solid">
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int elemType;
/************************************************************************/
/* 以下是关于队列链接存储操作的6种算法 */
/************************************************************************/
strUCt sNode{
elemType data; /* 值域 */
struct sNode *next; /* 链接指针 */
};
struct queueLK{
struct sNode *front; /* 队首指针 */
struct sNode *rear; /* 队尾指针 */
};
/* 1.初始化链队 */
void initQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
{
hq->front = hq->rear = NULL; /* 把队首和队尾指针置空 */
return;
}
/* 2.向链队中插入一个元素x */
void enQueue(struct queueLK *hq, elemType x)
{
/* 得到一个由newP指针所指向的新结点 */
struct sNode *newP;
newP = malloc(sizeof(struct sNode));
if(newP == NULL){
printf("内存空间分配失败! ");
exit(1);
}
/* 把x的值赋给新结点的值域,把新结点的指针域置空 */
newP->data = x;
newP->next = NULL;
/* 若链队为空,则新结点即是队首结点又是队尾结点 */
if(hq->rear == NULL){
hq->front = hq->rear = newP;
}else{ /* 若链队非空,则依次修改队尾结点的指针域和队尾指针,使之指向新的队尾结点 */
hq->rear = hq->rear->next = newP; /* 注重赋值顺序哦 */
}
return;
}
/* 3.从队列中删除一个元素 */
elemType outQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
{
struct sNode *p;
elemType temp;
/* 若链队为空则停止运行 */
if(hq->front == NULL){
printf("队列为空,无法删除! ");
exit(1);
}
temp = hq->front->data; /* 暂存队尾元素以便返回 */
p = hq->front; /* 暂存队尾指针以便回收队尾结点 */
hq->front = p->next; /* 使队首指针指向下一个结点 */
/* 若删除后链队为空,则需同时使队尾指针为空 */
if(hq->front == NULL){
hq->rear = NULL;
}
free(p); /* 回收原队首结点 */
return temp; /* 返回被删除的队首元素值 */
}
/* 4.读取队首元素 */
elemType peekQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
{
/* 若链队为空则停止运行 */
if(hq->front == NULL){
printf("队列为空,无法删除! ");
exit(1);
}
return hq->front->data; /* 返回队首元素 */
}
/* 5.检查链队是否为空,若为空则返回1, 否则返回0 */
int emptyQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
{
/* 判定队首或队尾任一个指针是否为空即可 */
if(hq->front == NULL){
return 1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
/* 6.清除链队中的所有元素 */
void clearQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
{
struct sNode *p = hq->front; /* 队首指针赋给p */
/* 依次删除队列中的每一个结点,最后使队首指针为空 */
while(p != NULL){
hq->front = hq->front->next;
free(p);
p = hq->front;
} /* 循环结束后队首指针已经为空 */
hq->rear = NULL; /* 置队尾指针为空 */
return;
}
/************************************************************************/
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct queueLK q;
int a[8] = {3, 8, 5, 17, 9, 30, 15, 22};
int i;
initQueue(&q);
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++){
enQueue(&q, a[i]);
}
printf("%d ", outQueue(&q)); printf("%d ", outQueue(&q));
enQueue(&q, 68);
printf("%d ", peekQueue(&q)); printf("%d ", outQueue(&q));
while(!emptyQueue(&q)){
printf("%d ", outQueue(&q));
}
printf(" ");
clearQueue(&q);
system("pause");
}
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int elemType;
/************************************************************************/
/* 以下是关于队列链接存储操作的6种算法 */
/************************************************************************/
strUCt sNode{
elemType data; /* 值域 */
struct sNode *next; /* 链接指针 */
};
struct queueLK{
struct sNode *front; /* 队首指针 */
struct sNode *rear; /* 队尾指针 */
};
/* 1.初始化链队 */
void initQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
{
hq->front = hq->rear = NULL; /* 把队首和队尾指针置空 */
return;
}
/* 2.向链队中插入一个元素x */
void enQueue(struct queueLK *hq, elemType x)
{
/* 得到一个由newP指针所指向的新结点 */
struct sNode *newP;
newP = malloc(sizeof(struct sNode));
if(newP == NULL){
printf("内存空间分配失败! ");
exit(1);
}
/* 把x的值赋给新结点的值域,把新结点的指针域置空 */
newP->data = x;
newP->next = NULL;
/* 若链队为空,则新结点即是队首结点又是队尾结点 */
if(hq->rear == NULL){
hq->front = hq->rear = newP;
}else{ /* 若链队非空,则依次修改队尾结点的指针域和队尾指针,使之指向新的队尾结点 */
hq->rear = hq->rear->next = newP; /* 注重赋值顺序哦 */
}
return;
}
/* 3.从队列中删除一个元素 */
elemType outQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
{
struct sNode *p;
elemType temp;
/* 若链队为空则停止运行 */
if(hq->front == NULL){
printf("队列为空,无法删除! ");
exit(1);
}
temp = hq->front->data; /* 暂存队尾元素以便返回 */
p = hq->front; /* 暂存队尾指针以便回收队尾结点 */
hq->front = p->next; /* 使队首指针指向下一个结点 */
/* 若删除后链队为空,则需同时使队尾指针为空 */
if(hq->front == NULL){
hq->rear = NULL;
}
free(p); /* 回收原队首结点 */
return temp; /* 返回被删除的队首元素值 */
}
/* 4.读取队首元素 */
elemType peekQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
{
/* 若链队为空则停止运行 */
if(hq->front == NULL){
printf("队列为空,无法删除! ");
exit(1);
}
return hq->front->data; /* 返回队首元素 */
}
/* 5.检查链队是否为空,若为空则返回1, 否则返回0 */
int emptyQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
{
/* 判定队首或队尾任一个指针是否为空即可 */
if(hq->front == NULL){
return 1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
/* 6.清除链队中的所有元素 */
void clearQueue(struct queueLK *hq)
{
struct sNode *p = hq->front; /* 队首指针赋给p */
/* 依次删除队列中的每一个结点,最后使队首指针为空 */
while(p != NULL){
hq->front = hq->front->next;
free(p);
p = hq->front;
} /* 循环结束后队首指针已经为空 */
hq->rear = NULL; /* 置队尾指针为空 */
return;
}
/************************************************************************/
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct queueLK q;
int a[8] = {3, 8, 5, 17, 9, 30, 15, 22};
int i;
initQueue(&q);
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++){
enQueue(&q, a[i]);
}
printf("%d ", outQueue(&q)); printf("%d ", outQueue(&q));
enQueue(&q, 68);
printf("%d ", peekQueue(&q)); printf("%d ", outQueue(&q));
while(!emptyQueue(&q)){
printf("%d ", outQueue(&q));
}
printf(" ");
clearQueue(&q);
system("pause");
}
 更多内容请看C/C++进阶技术文档 数据结构 数据结构相关文章专题,或
更多内容请看C/C++进阶技术文档 数据结构 数据结构相关文章专题,或
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int elemType;
/************************************************************************/
/* 以下是关于队列顺序存储操作的6种算法 */
/************************************************************************/
struct queue{
elemType *queue; /* 指向存储队列的数组空间 */
int front, rear, len; /* 队首指针(下标),队尾指针(下标),队列长度变量 */
int maxSize; /* queue数组长度 */
};
void againMalloc(struct queue *q)
{
/* 空间扩展为原来的2倍,原内容被自动拷贝到p所指向的存储空间中 */
elemType *p;
p = realloc(q->queue, 2 * q->maxSize * sizeof(elemType));
/* 动态存储空间分配,若失败则退出运行 */
if(!p){
printf("空间分配失败! ");
exit(1);
}
q->queue = p; /* 使queue指向新的队列空间 */
/* 把原队列的尾部内容后移maxSize个位置 */
if(q->rear != q->maxSize -1){
int i;
for(i = 0; i <= q->rear; i++){
q->queue[i+q->maxSize] = q->queue[i];
}
q->rear += q->maxSize; /* 队尾指针后移maxSize个位置 */
}
q->maxSize = 2 * q->maxSize; /* 把队列空间大小修改为新的长度 */
return;
}
/* 1.初始化队列 */
void initQueue(struct queue *q, int ms)
{
/* 检查ms是否有效,若无效则退出运行 */
if(ms <= 0){
printf("ms值非法!
");
exit(1);
}
q->maxSize = ms; /* 置队列空间大小为ms */
/* 动态存储空间分配,若失败则退出运行 */
q->queue = malloc(ms * sizeof(elemType));
if(!q->queue){
printf("内存空间分配失败! ");
exit(1);
}
q->front = q->rear = 0; /* 初始置队列为空 */
return;
}
/* 2.向队列中插入元素x */
void enQueue(struct queue *q, elemType x)
{
/* 当队列满时进行动态生分配 */
if((q->rear + 1) % q->maxSize == q->front){
againMalloc(q);
}
q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % q->maxSize; /* 求出队尾的下一个位置 */
q->queue[q->rear] = x; /* 把x的值赋给新的队尾 */
return;
}
/* 3.从队列中删除元素并返回 */
elemType outQueue(struct queue *q)
{
/* 若队列为空则终止运行 */
if(q->front == q->rear){
printf("队列为空,无法删除! ");
exit(1);
}
q->front = (q->front +1) % q->maxSize; /* 使队首指针指向下一个位置 */
return q->queue[q->front]; /* 返回队首元素 */
}
/* 4.读取队首元素,不改变队列状态 */
elemType peekQueue(struct queue *q)
{
/* 若队列为空则终止运行 */
if(q->front == q->rear){
printf("队列为空,无法删除! ");
exit(1);
}
return q->queue[(q->front +1) % q->maxSize];/* 队首元素是队首指针的下一个位置中的元素 */
}
/* 5.检查一个队列是否为空,若是则返回1,否则返回0 */
int emptyQueue(struct queue *q)
{
if(q->front == q->rear){
return 1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
/* 6.清除一个队列,并释放动态存储空间 */
void clearQueue(struct queue *q)
{
if(q->queue !
= NULL){
free(q->queue);
q->queue = NULL; /* 设置队列空间指针为空 */
q->front = q->rear = 0; /* 设置队列为空 */
q->maxSize = 0; /* 设置队列大小为0 */
}
return;
}
/************************************************************************/
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct queue q;
int a[8] = {3, 8, 5, 17, 9, 30, 15, 22};
int i;
initQueue(&q, 5);
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++){
enQueue(&q, a[i]);
}
printf("%d ", outQueue(&q)); printf("%d ", outQueue(&q));
enQueue(&q, 68);
printf("%d ", peekQueue(&q)); printf("%d ", outQueue(&q));
while(!emptyQueue(&q)){
printf("%d ", outQueue(&q));
}
printf(" ");
clearQueue(&q);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int elemType;
/************************************************************************/
/* 以下是关于队列顺序存储操作的6种算法 */
/************************************************************************/
struct queue{
elemType *queue; /* 指向存储队列的数组空间 */
int front, rear, len; /* 队首指针(下标),队尾指针(下标),队列长度变量 */
int maxSize; /* queue数组长度 */
};
void againMalloc(struct queue *q)
{
/* 空间扩展为原来的2倍,原内容被自动拷贝到p所指向的存储空间中 */
elemType *p;
p = realloc(q->queue, 2 * q->maxSize * sizeof(elemType));
/* 动态存储空间分配,若失败则退出运行 */
if(!p){
printf("空间分配失败! ");
exit(1);
}
q->queue = p; /* 使queue指向新的队列空间 */
/* 把原队列的尾部内容后移maxSize个位置 */
if(q->rear != q->maxSize -1){
int i;
for(i = 0; i <= q->rear; i++){
q->queue[i+q->maxSize] = q->queue[i];
}
q->rear += q->maxSize; /* 队尾指针后移maxSize个位置 */
}
q->maxSize = 2 * q->maxSize; /* 把队列空间大小修改为新的长度 */
return;
}
/* 1.初始化队列 */
void initQueue(struct queue *q, int ms)
{
/* 检查ms是否有效,若无效则退出运行 */
if(ms <= 0){
printf("ms值非法!
");
exit(1);
}
q->maxSize = ms; /* 置队列空间大小为ms */
/* 动态存储空间分配,若失败则退出运行 */
q->queue = malloc(ms * sizeof(elemType));
if(!q->queue){
printf("内存空间分配失败! ");
exit(1);
}
q->front = q->rear = 0; /* 初始置队列为空 */
return;
}
/* 2.向队列中插入元素x */
void enQueue(struct queue *q, elemType x)
{
/* 当队列满时进行动态生分配 */
if((q->rear + 1) % q->maxSize == q->front){
againMalloc(q);
}
q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % q->maxSize; /* 求出队尾的下一个位置 */
q->queue[q->rear] = x; /* 把x的值赋给新的队尾 */
return;
}
/* 3.从队列中删除元素并返回 */
elemType outQueue(struct queue *q)
{
/* 若队列为空则终止运行 */
if(q->front == q->rear){
printf("队列为空,无法删除! ");
exit(1);
}
q->front = (q->front +1) % q->maxSize; /* 使队首指针指向下一个位置 */
return q->queue[q->front]; /* 返回队首元素 */
}
/* 4.读取队首元素,不改变队列状态 */
elemType peekQueue(struct queue *q)
{
/* 若队列为空则终止运行 */
if(q->front == q->rear){
printf("队列为空,无法删除! ");
exit(1);
}
return q->queue[(q->front +1) % q->maxSize];/* 队首元素是队首指针的下一个位置中的元素 */
}
/* 5.检查一个队列是否为空,若是则返回1,否则返回0 */
int emptyQueue(struct queue *q)
{
if(q->front == q->rear){
return 1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
/* 6.清除一个队列,并释放动态存储空间 */
void clearQueue(struct queue *q)
{
if(q->queue !
= NULL){
free(q->queue);
q->queue = NULL; /* 设置队列空间指针为空 */
q->front = q->rear = 0; /* 设置队列为空 */
q->maxSize = 0; /* 设置队列大小为0 */
}
return;
}
/************************************************************************/
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct queue q;
int a[8] = {3, 8, 5, 17, 9, 30, 15, 22};
int i;
initQueue(&q, 5);
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++){
enQueue(&q, a[i]);
}
printf("%d ", outQueue(&q)); printf("%d ", outQueue(&q));
enQueue(&q, 68);
printf("%d ", peekQueue(&q)); printf("%d ", outQueue(&q));
while(!emptyQueue(&q)){
printf("%d ", outQueue(&q));
}
printf(" ");
clearQueue(&q);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
 更多内容请看C/C++进阶技术文档 数据结构 数据结构相关文章专题,或
更多内容请看C/C++进阶技术文档 数据结构 数据结构相关文章专题,或精彩图集
精彩文章