C语言程序应用举例[图]
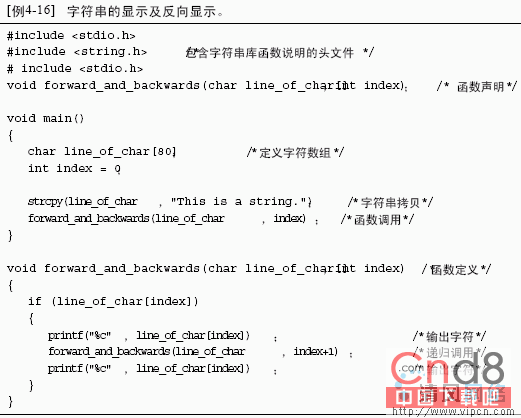
这是一个递归函数调用的例子。程序中函数f o r w a r d _ a n d _ b a c k w a r d s ( )的功能是显示一个字符串后反向显示该字符串。
[例4-17] 计算1~7的平方及平方和。
#include
# include
void header(); / *函数声明* /
void square(int number);
void ending();
int sum; /* 全局变量* /
m a i n ( )
{
int index;
h e a d e r ( ) ; / *函数调用* /
for (index = 1;index <= 7;i n d e x + + )
s q u a r e ( i n d e x ) ;
e n d i n g ( ) ; / *结束* /
}
void header()
{
sum = 0; /* 初始化变量"sum" */
printf("This is the header for the square program
;
")
}
void square(int number)
{
int numsq;
numsq = number * numbe;r
sum += numsq;
printf("The square of %d is %d,nn"u m b e r ,nu m s q ) ;
}
void ending()
{
printf("
The sum of the squares is %d,
s"u m ) ;
}
运行程序:
R U N ¿
This is the header for the square program
The square of 1 is 1
The square of 2 is 4
The square of 3 is 9
The square of 4 is 16
The square of 5 is 25
The square of 6 is 36
The square of 7 is 49
The sum of the squares is 140
这个程序打印出1到7的平方值,最后打印出1到7的平方值的和,其中全局变量s u m在多个
函数中出现过。
全局变量在h e a d e r中被初始化为零;在函数s q u a r e中,s u m对n u m b e r的平方值进行累加,也就是说,每调用一次函数s q u a r e和s u m就对n u m b e r的平方值累加一次;全局变量s u m在函数
e n d i n g中被打印。
[例4-18] 全局变量与局部变量的作用。
#include
void head1(void);
void head2(void);
void head3(void);
int count; /* 全局变量* /
m a i n ( )
{
register int index; / *定义为主函数寄存器变量* /
h e a d 1 ( ) ;
h e a d 2 ( ) ;
h e a d 3 ( ) ;
for (index = 8;index > 0;index--) /* 主函数"for" 循环* /
{
int stuff; /* 局部变量* /
/* 这种变量的定义方法在Turbo C 中是不答应的* /
/* stuff 的可见范围只在当前循环体内* /
for(stuff = 0;stuff <= 6;s t u f f + + )
printf("%d ",s t u f f ) ;
printf(" index is now %d,n"in d e x ) ;
}
}
int counter; /* 全局变量* /
/* 可见范围为从定义之处到源程序结尾* /
void head1(void)
{
int index; / * 此变量只用于head1 */
index = 23;
printf("The header1 value is %d,n"in d e x ) ;
}
void head2(void)
{
int count; /* 此变量是函数h e a d 2 ( ) 的局部变量* /
/* 此变量名与全局变量c o u n t 重名* /
/* 故全局变量c o u n t 不能在函数h e a d 2 ( ) 中使用* /
count = 53;
printf("The header2 value is %d,n"co u n t ) ;
counter = 77;
}
void head3(void)
{
printf("The header3 value is %d,nc"o u n t e r ) ;
}
运行程序:
R U N ¿
The headerl value is 23
The header2 value is 53
The header3 value is 77
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 index is now 8
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 index is now 7
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 index is now 6
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 index is now 5
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 index is now 4
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 index is now 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 index is now 2
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 index is now 1
该程序的演示帮助读者来了解全局变量、局部变量的作用域,请仔细理解体会。