链表的c语言实现(八)
2、插入
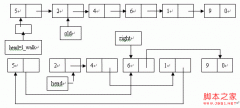
对于双向循环链表,我们现在可以随意地在某已知结点p前或者p后插入一个新的结点。
假若s,p,q是连续三个结点的指针,若我们要在p前插入一个新结点r,则只需把s的右链域指针指向r,r的左链域指针指向s,r的右链域指针指向p,p的左链域指针指向r即可。
在p,q之间插入原理也一样。
下面就是一个应用双向循环链表插入算法的例子:
#include
#include
#include
#define N 10
typedef strUCt node
{
char name[20];
struct node *llink,*rlink;
}stud;
stud * creat(int n)
{
stud *p,*h,*s;
int i;
if((h=(stud *)malloc(sizeof(stud)))==NULL)
{
printf("不能分配内存空间!");
exit(0);
}
h->name[0]='\0';
h->llink=NULL;
h->rlink=NULL;
p=h;
for(i=0;i { if((s= (stud *) malloc(sizeof(stud)))==NULL) { printf("不能分配内存空间!"); exit(0); } p->rlink=s; printf("请输入第%d个人的姓名",i+1); scanf("%s",s->name); s->llink=p; s->rlink=NULL; p=s; } h->llink=s; p->rlink=h; return(h); } stud * search(stud *h,char *x) { stud *p; char *y; p=h->rlink; while(p!=h) { y=p->name; if(strcmp(y,x)==0) return(p); else p=p->rlink; } printf("没有查找到该数据!"); } void print(stud *h) { int n; stud *p; p=h->rlink; printf("数据信息为: "); while(p!=h) { printf("%s ",&*(p->name)); p=p->rlink; } printf(" "); } void insert(stud *p) { char stuname[20]; stud *s; if((s= (stud *) malloc(sizeof(stud)))==NULL) { printf("不能分配内存空间!"); exit(0); } printf("请输入你要插入的人的姓名:"); scanf("%s",stuname); strcpy(s->name,stuname); s->rlink=p->rlink; p->rlink=s; s->llink=p; (s->rlink)->llink=s; } main() { int number; char studname[20]; stud *head,*searchpoint; number=N; clrscr(); head=creat(number); print(head); printf("请输入你要查找的人的姓名:"); scanf("%s",studname); searchpoint=search(head,studname); printf("你所要查找的人的姓名是:%s ",*&searchpoint->name); insert(searchpoint); print(head); }
- 上一篇:C语言的程序结构[组图]
- 下一篇:链表的c语言实现(九)